Alcohol Use Disorder & Cannabis Treatment
Aug 27, 2025
By Berta Kaguako, Mental Health and Substance Misuse Consultant
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is one of the most challenging addictions to treat, with high relapse rates and treatment options that often come with significant side effects. Traditional detoxification relies on benzodiazepines, such as Librium, which can effectively manage withdrawal symptoms but carry risks like dependence and sedation. Given these limitations, alternative therapies are being explored. Medical Cannabis, particularly cannabidiol (CBD), shows early promise in reducing cravings, easing withdrawal, and protecting the brain. This report examines AUD, current treatments, and emerging evidence for Cannabis-based approaches.
What is Alcohol Use Disorder?
AUD is a chronic, relapsing condition that affects millions worldwide and creates profound health, social, and economic burdens. It is characterised by an impaired ability to control alcohol use despite adverse consequences.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), defines AUD by eleven criteria, including tolerance, withdrawal, cravings, and continued use despite harm. Severity ranges from mild to severe based on criteria met within a year.
In the U.S., approximately 14 to 15 million adults suffer from AUD, contributing to over three million deaths globally each year. Beyond physical harms such as liver disease and cancer, AUD impacts relationships, employment, and finances, resulting in billions of dollars in economic costs.
Traditional therapies save lives, but relapse remains high, pushing researchers to explore complementary options like medical Cannabis.
📚 Deep Dive: Complete NHS Guide to Alcohol Misuse
Treatment for Alcohol Use Disorder
Treatment for AUD typically involves behavioural therapies such as Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) and medications approved by the FDA, including naltrexone, acamprosate, and disulfiram. These medications target different aspects of alcohol dependence and relapse prevention. Detoxification, or “detox,” is the initial phase for managing acute withdrawal symptoms safely.
How is AUD commonly treated?
Librium (chlordiazepoxide) is a long-acting benzodiazepine commonly used during detox to reduce withdrawal severity and prevent complications such as seizures or delirium tremens. It works by enhancing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a calming neurotransmitter in the brain, thus counteracting the nervous system hyper-excitability caused by alcohol cessation.
Treatment typically involves an initial high dose that is tapered over 3–7 days, often supplemented with thiamine and fluids to address deficiencies.
Although effective, Librium carries risks of sedation and dependency, so its use is limited to short-term medical supervision during detoxification. After detox, patients usually transition to counselling, behavioural therapies, and medications aimed at supporting abstinence and reducing cravings.
How Can Cannabis Be Used to Manage Alcoholism?
Medical Cannabis, particularly cannabidiol (CBD), has attracted interest as a potential adjunct or alternative for managing AUD symptoms. CBD is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid, in contrast to tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which produces intoxicating effects. Preclinical studies suggest CBD may reduce alcohol consumption, mitigate relapse-related behaviours, and protect against alcohol-induced brain and liver damage.
Additionally, CBD has shown promise in alleviating anxiety, irritability, and insomnia common during alcohol withdrawal. Unlike benzodiazepines, Cannabis products high in CBD and low in THC might offer a milder, less dependency-prone option for some individuals under medical supervision. Psychological benefits are also notable: CBD may ease anxiety and depression, which often co-occur with AUD and contribute to relapse.
A small clinical trial observed that some participants reduced their alcohol intake when substituting Cannabis, highlighting its potential as a harm reduction tool. However, THC-dominant products can impair cognition, increase anxiety, and carry a mild risk of dependency, especially in vulnerable populations. Large-scale, controlled clinical trials are still needed to confirm safety, efficacy, and best clinical practices.
Risks and Limitations
While CBD shows therapeutic promise, THC-rich Cannabis can produce adverse cognitive and psychological effects, warranting caution in its use for AUD. Advice would be to follow standard protocols for managing psychoactive medications in general.
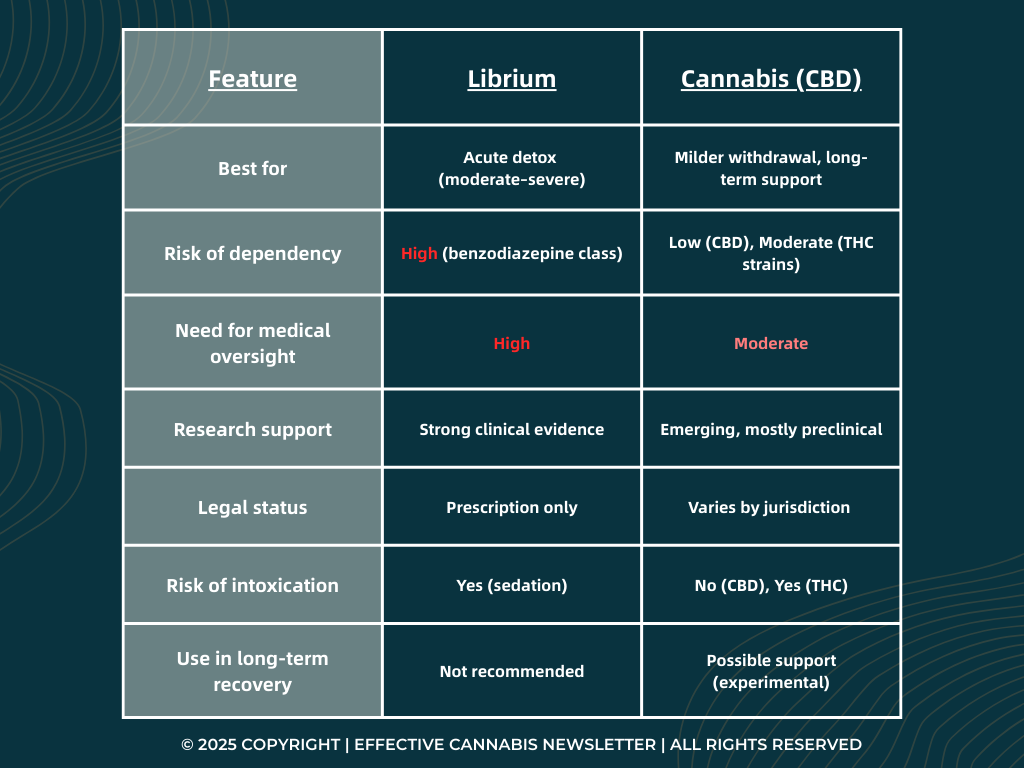
Librium vs Cannabis
As the treatment landscape for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) continues to evolve, both traditional and emerging therapies are being examined for their effectiveness in managing withdrawal symptoms and supporting recovery. Librium (chlordiazepoxide), a long-established benzodiazepine, is widely used during acute alcohol detox to prevent severe complications like seizures and delirium tremens.
In contrast, medical Cannabis, particularly cannabidiol (CBD), has gained attention as a potential alternative or complementary option due to its anxiolytic, neuroprotective, and anti-craving properties. While both substances act on the central nervous system, they differ significantly in terms of mechanism, risk profile, clinical evidence, and long-term applicability.
The following comparison explores the benefits and limitations of Librium and Cannabis in the treatment of AUD, helping to clarify their respective roles in both detoxification and long-term recovery.


Conclusion
Alcohol Use Disorder remains a complex condition with substantial treatment challenges. While Librium remains a cornerstone for safely managing acute withdrawal, its limitations underscore the urgent need for new, safer options.
Medical Cannabis, especially CBD-rich formulations, offers a promising avenue to support recovery with potentially fewer side effects. However, more rigorous research, standardized protocols, and clear regulations are essential before Cannabis can be widely integrated into AUD care.
Patients deserve safer, evidence-based treatment options. It is time to invest seriously in Cannabis research for AUD, so recovery becomes more compassionate, effective, and accessible.
References & Further Reading
Dive deeper into the science behind Cannabis-assisted addiction treatment
🧠 Clinical Research & Evidence
PubMed Research Study (2018)
Cannabidiol as a Novel Candidate Alcohol Use Disorder Pharmacotherapy: A Systematic Review
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30698831/
Clinical Trial Data (2025)
A preliminary randomized trial of the safety, tolerability, and clinical effects of hemp-derived cannabidiol in alcohol use disorder
Frontiers in Psychiatry - Latest Research
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychiatry/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1516351/full
📊 Epidemiological & Treatment Outcome Studies
Preliminary Clinical Trial (Pre-print) (2019)
Characteristics of Patients that Substitute Medical Cannabis for Alcohol
medRxiv - Early Stage Research
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/19003798v1
SAGE Journals - Treatment Analysis (2015)
Cannabidiol as an Intervention for Addictive Behaviors: A Systematic Review of the Evidence
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.4137/SART.S25081
ScienceDirect - Addiction Medicine (2024)
Cannabis substitution effects in alcohol-dependent populations
The neurobehavioural effects of cannabidiol in alcohol use disorder: Study protocol for a double-blind, randomised, crossover, placebo-controlled trial
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2451865424000887
🏥 Clinical Guidelines & Healthcare Resources
National Health Service (NHS) - United Kingdom
Comprehensive guide to alcohol misuse recognition and treatment
Official Medical Guidelines
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/alcohol-misuse/
University of Victoria - Centre for Addictions Research
Cannabis and alcohol: Service provider perspectives and implementation
Canadian Implementation Research https://www.uvic.ca/research/centres/cisur/assets/docs/maps-cop/cmaps-alcohol-cannabis-service-providers-web.pdf
🌿 Patient Education & Harm Reduction Resources
Presto Doctor (2025)
Cannabis for alcohol consumption reduction: Patient-focused information
Clinical Practice Resource
https://prestodoctor.com/content/general/cannabis-alcohol-can-cannabis-reduce-alcohol-consumption
About Berta Kaguako:
Berta Kaguako is a Mental Health and Substance Misuse Consultant with an Undergraduate in Psychotherapy and a Master's in Psychoanalysis. Berta’s background is in Mental Health, Substance Misuse and Children & Families: in both a therapeutic and senior management capacity, having won 3x Blooming Strong Awards (Recognition from UN for contribution to violence against Women). Berta is also the Co-Founder and Managing Director for EthVida, and independently runs the wellbeing service / educational platform.
Click the Learn More Button
Effective Cannabis Newsletter is a platform to educate on the vital role of the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) in one's health. The information is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. All content, including text, graphics, images, and information, contained in or available through this newsletter is for general information purposes only. It is not medical advice; it is health awareness.
Were you moved or inspired by a piece of content?
Do you have a suggestion or question for us?
Do you have a powerful story about your health and Cannabis?
Click the button and let us know!




